MeshRepair Documentation
3D Mesh Repair
MeshRepair Documentation
Automatic mesh hole detection and filling for 3D scanning, game development, and additive manufacturing workflows
Overview
MeshRepair is an open-source tool for detecting and filling holes in triangulated 3D meshes. It provides both a command-line interface for batch processing and a Blender addon for interactive use.
Project Background
This tool was developed to address a common issue in photogrammetry workflows:
The Problem with Photogrammetry Output
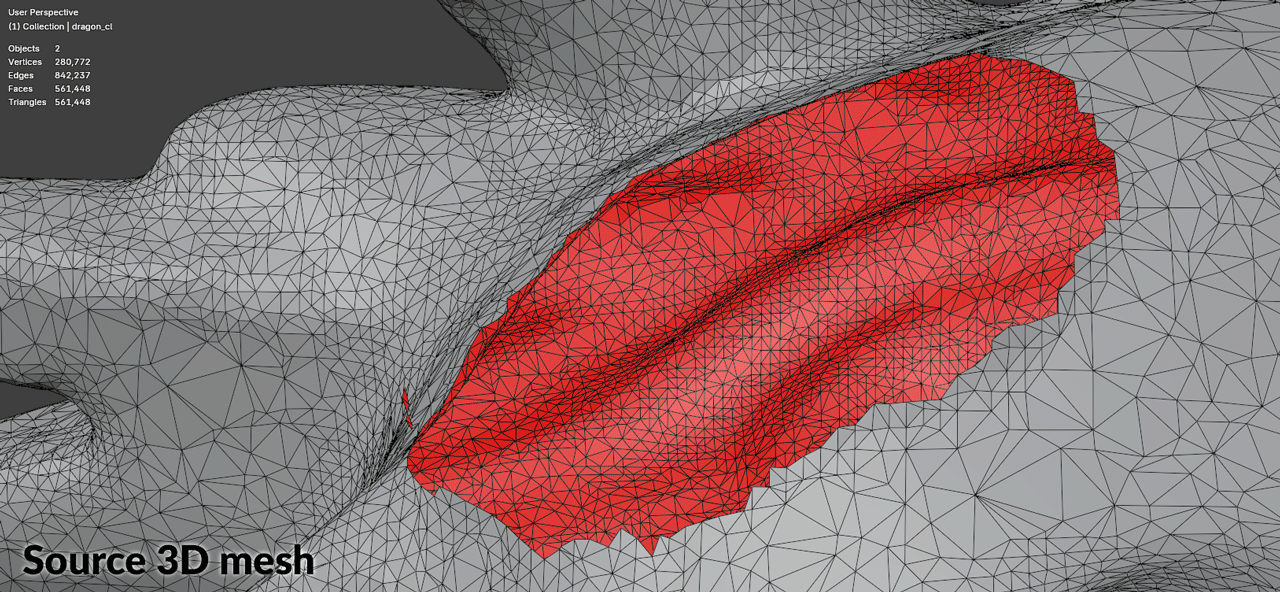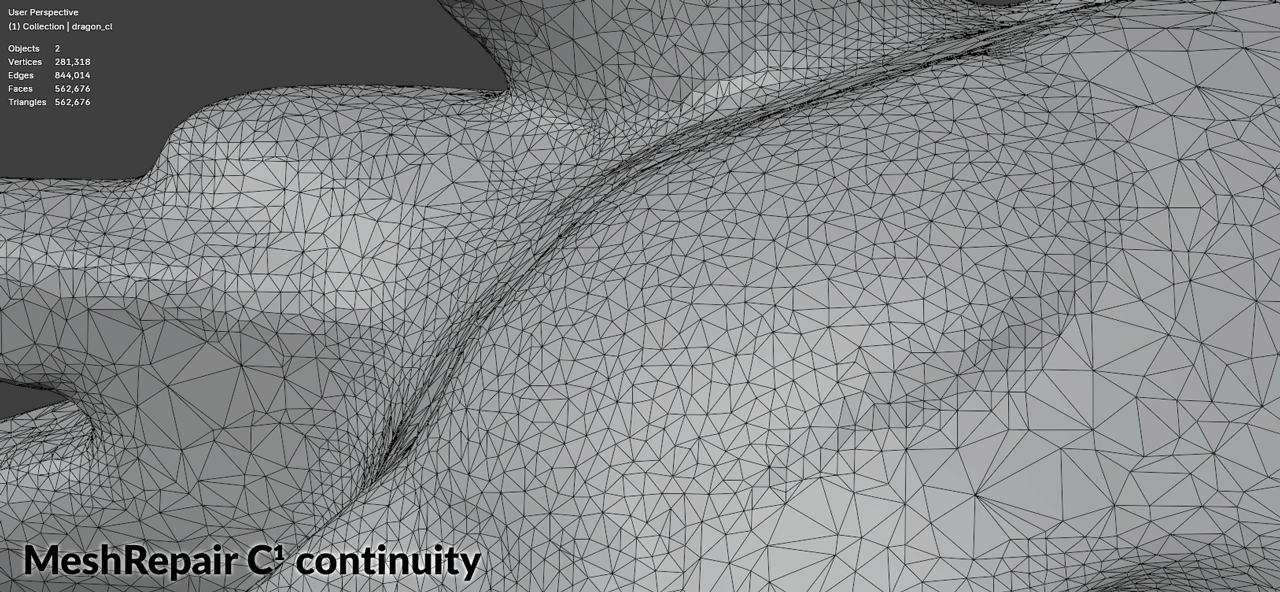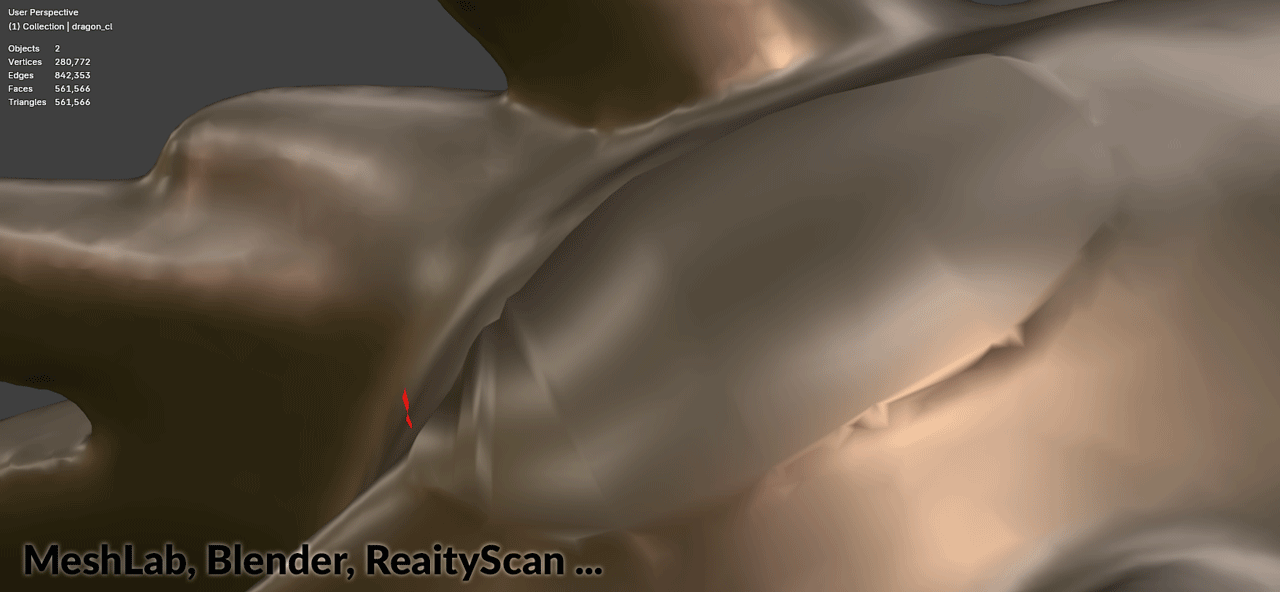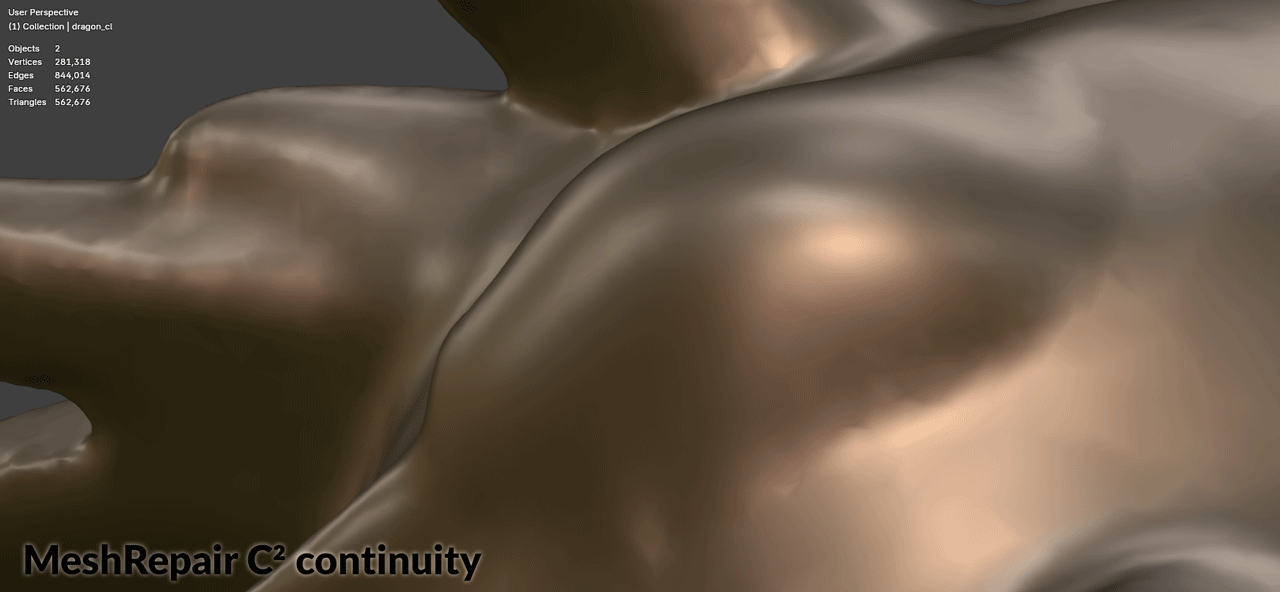
Software such as Epic’s RealityScan (formerly RealityCapture) and similar photogrammetry applications generate watertight meshes by creating large polygons to close open boundaries. These oversized polygons typically appear in:
| Area | Cause |
|---|---|
| Mesh boundaries | Large triangles spanning the capture edge |
| Low overlap regions | Oversized faces where few source images overlap |
| Weak depth reconstruction | Large polygons masking areas with poor 3D data |
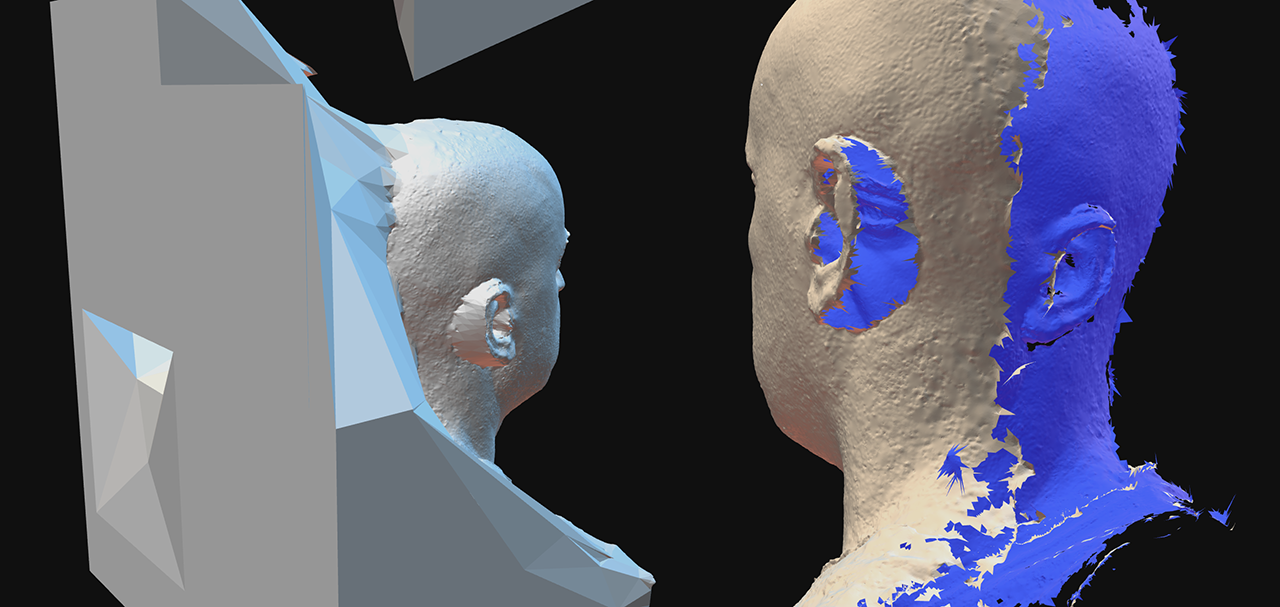
Impact on Downstream Processing
These oversized polygons create problems for subsequent operations:
- Sculpting: Inconsistent polygon sizes cause uneven brush behavior
- Retopology/Wrapping: Automatic retopology tools produce poor results on mixed-density meshes
- UV Mapping: Extreme size differences lead to texture distortion
- Subdivision: Non-uniform polygon sizes create uneven mesh density
Intended Workflow
The recommended approach is to remove problematic oversized polygons (creating holes) and then fill those holes with properly-sized geometry:
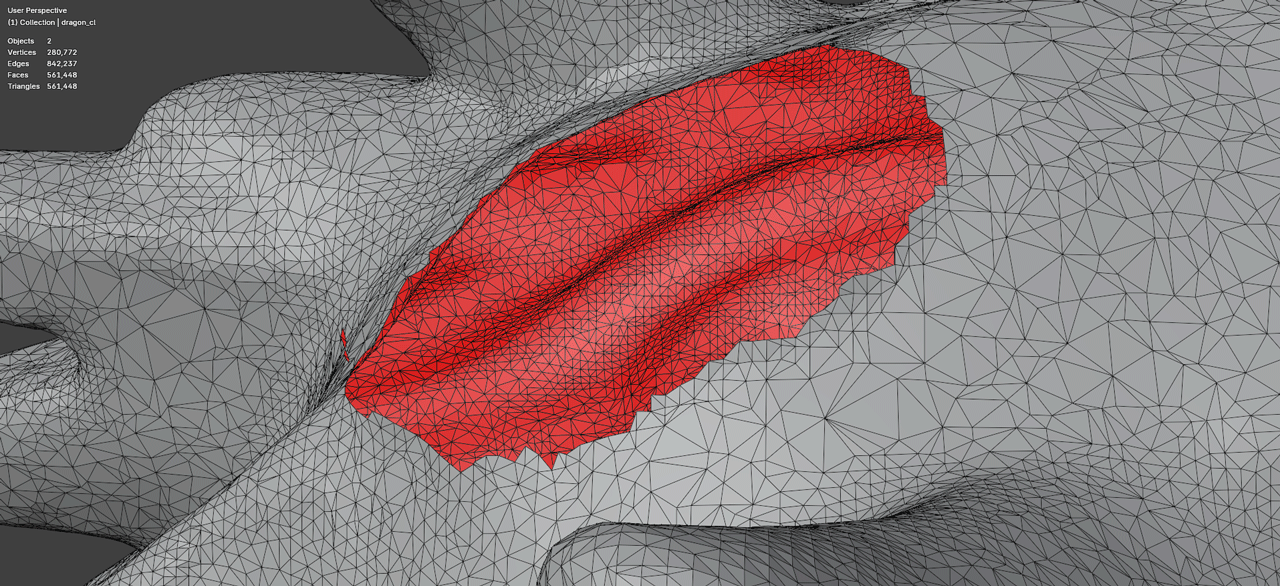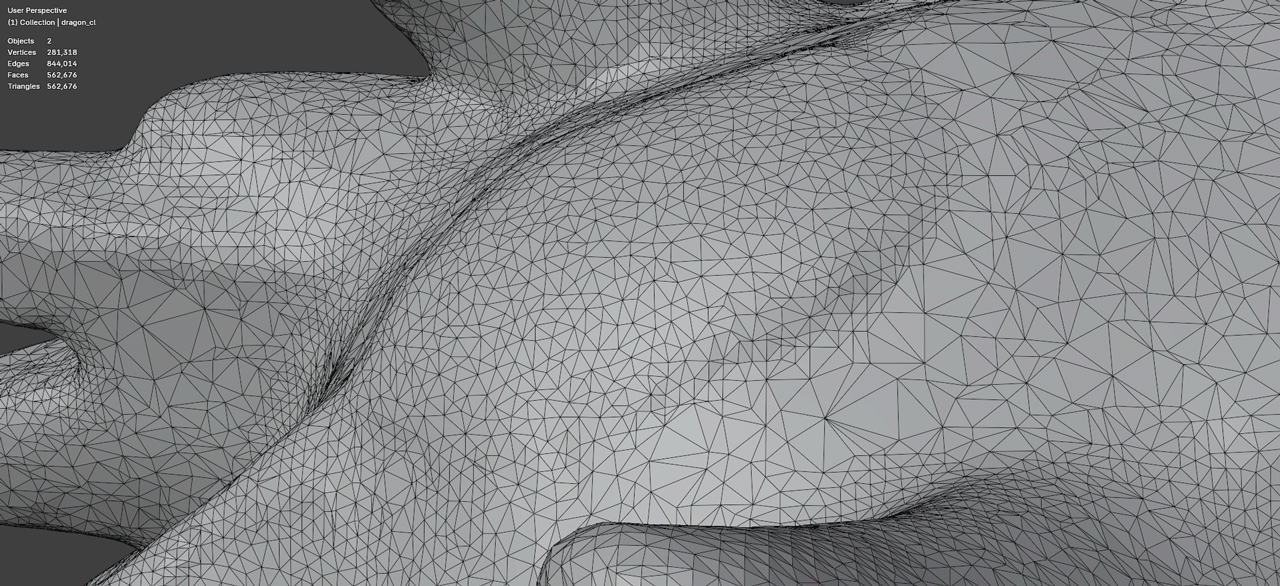
MeshRepair generates fill geometry with:
- Triangle sizes matching the surrounding mesh density
- Smooth surface continuity with existing geometry
- Clean topology suitable for further processing
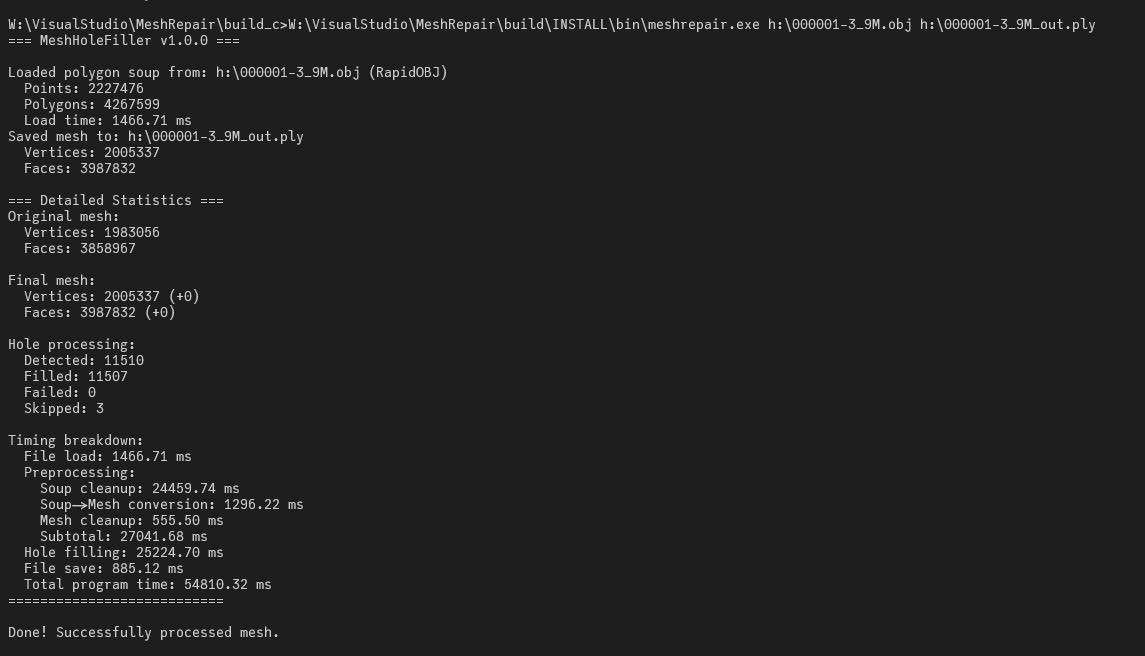
High-Polygon Mesh Support
Photogrammetry outputs frequently contain millions of polygons. MeshRepair is designed to handle large meshes efficiently:
- Multi-threaded hole filling with automatic workload distribution
- Memory-efficient partitioned processing
- Optimized OBJ/PLY file loading
- Blender Edit Mode support for processing mesh sections
Recommended Workflow
Photogrammetry (RealityScan, Metashape, 3DF Zephir, ...)
-> Remove oversized boundary polygons (RealityScan, Metashape, Blender, ...)
-> MeshRepair CLI or Addon (fill holes with uniform geometry)
-> Continue with sculpting, retopology, or mesh wrapping
Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Hole Detection | Identifies all boundary loops in the mesh |
| Hole Filling | Triangulates holes using constrained Delaunay methods |
| Mesh Preprocessing | Removes duplicate vertices, non-manifold geometry, and isolated components |
| Surface Continuity | Supports C⁰, C¹, and C² continuity for filled regions |
| Blender Integration | Native addon with Edit Mode selection support |
| Command Line Interface | Batch processing and scripting support |
| Multi-threaded Processing | Parallel hole filling with partition count capped by hole count |
| Partition Tuning | Minimum edge budget per partition (--min-edges) to avoid oversharding tiny holes |
| Global Hole Size Guards | Diameter limits use the full mesh bounding box even when partitioned |
Tools
Command Line Interface
For batch processing, automation, and integration with other tools.
meshrepair input.obj output.obj
Blender Addon
For interactive use within Blender’s modeling environment.
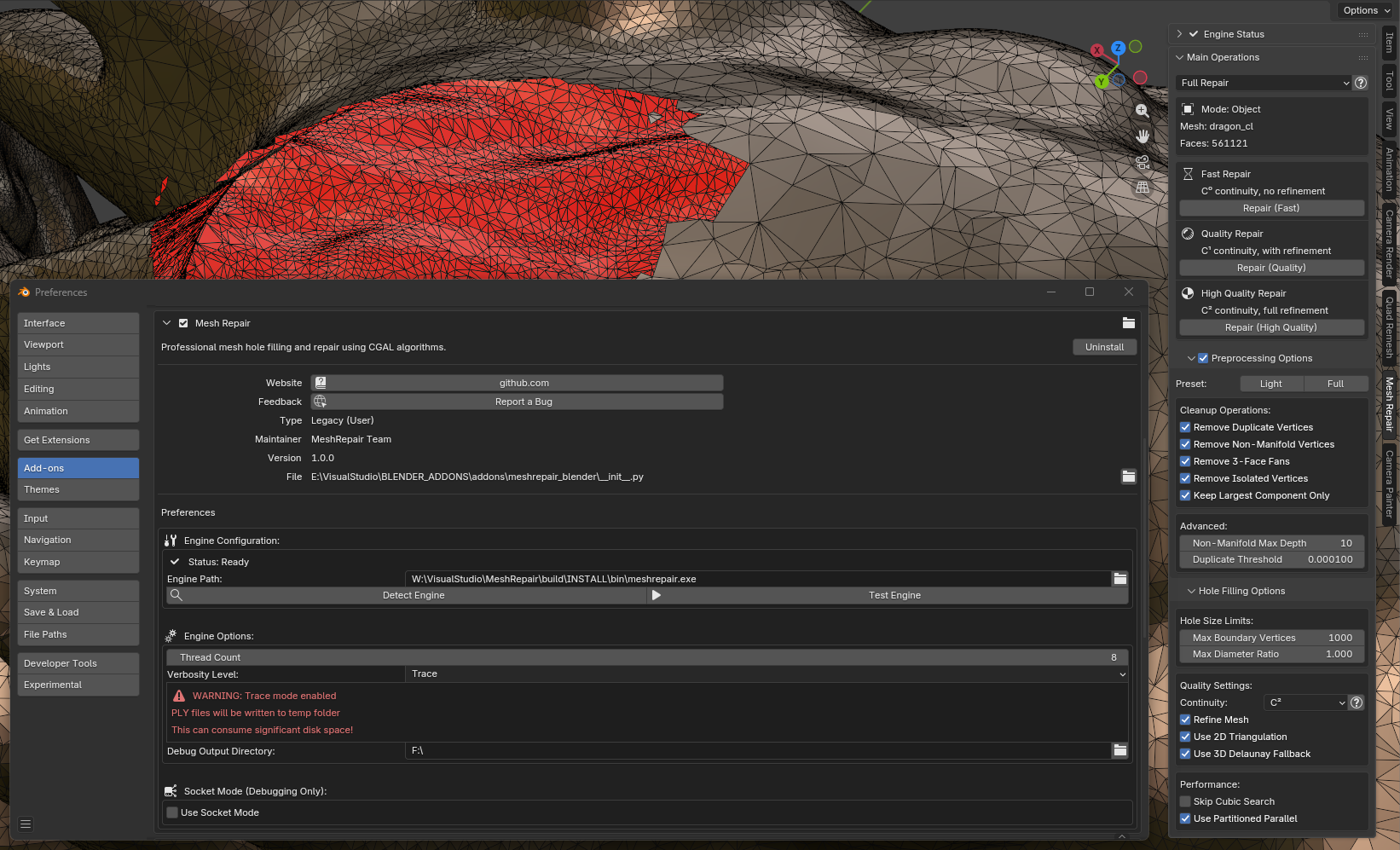
Provides direct access to repair operations from Blender’s sidebar panel.
Technical Overview
MeshRepair processes meshes through four stages:
1. Preprocessing
Cleans mesh topology by removing duplicate vertices, non-manifold elements, isolated vertices, and small disconnected components.
2. Hole Detection
Identifies all boundary loops (holes) by traversing border halfedges in the mesh structure.
3. Hole Filling
Fills each hole using the Liepa algorithm with constrained Delaunay triangulation and optional Laplacian fairing for surface smoothness.
4. Output
Exports the repaired mesh in the specified format.
Surface Continuity Levels
The hole filling algorithm supports three continuity levels:
| Level | Description | Computation Cost | Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| C⁰ | Positional continuity | Low | Fast processing, preview |
| C¹ | Tangent continuity | Medium | General use |
| C² | Curvature continuity | High | High-quality output |

System Requirements
Minimum
- OS: Windows 10, Linux (Ubuntu 20.04+), macOS 11+
- RAM: 4 GB
- CPU: Dual-core processor
- Blender: 3.3+ (for addon)
Recommended
- RAM: 16 GB
- CPU: 8+ cores (for multi-threaded processing)
- Storage: SSD (for large mesh files)
Documentation
| Document | Description |
|---|---|
| CLI Guide | Command line interface usage |
| Blender Addon Guide | Blender addon installation and usage |
Support
- Issue Tracker: GitHub Issues
License
MeshRepair is released under the LGPL-2.1 license license. MeshRepair Blender addon is released under the GPL-2.0 license license.
Dependencies:
- CGAL - Computational geometry algorithms
- Eigen - Linear and sparse matrix computations
- nlohmann/json - JSON parsing
- RapidOBJ - OBJ file loading
References
Hole filling algorithm based on:
Peter Liepa. “Filling Holes in Meshes.” Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing, 2003.
Fairing algorithm based on:
Mario Botsch et al. “On Linear Variational Surface Deformation Methods.” IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2008.